محافظت در برابر DDoS چیست ؟
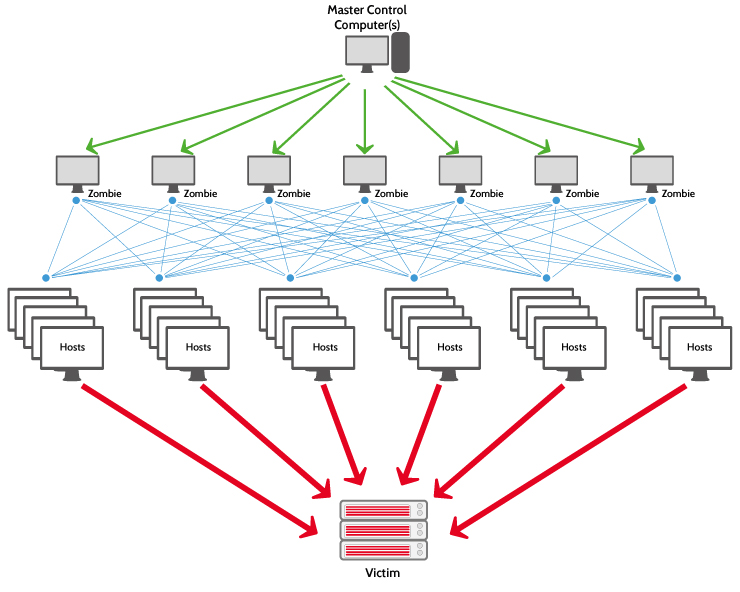
عملکرد یک حمله DDoS
شانس هدف قرارگرفتن یک سیستم بزرگ در برابر حملات DDoS بسیار زیاد و متعدد می باشد.
هدف حملات DDoS شناسایی یک سرور، سرویس یا زیرساخت و غیرقابل دسترس کردن آن با انجام عملیات سرریزی پهنای باند سرور یا به انحصار در آوردن منابع آن سیستم تا زمان تخلیه کامل از منابع می باشد.
در زمان حملات DDoS تعداد بسیار درخواست به صورت همزمان از نقاط مختلف اینترنت به سمت شما ارسال می شود.
شدت آتش گلوله یا تیراندازی به حدی می باشد که سرویس شما غیرقابل استفاده و یا بدتر از آن به طور کامل از دسترس خارج می شود.
ما چه پیشنهادی به شما برای محافظت از سرویس تان می دهیم
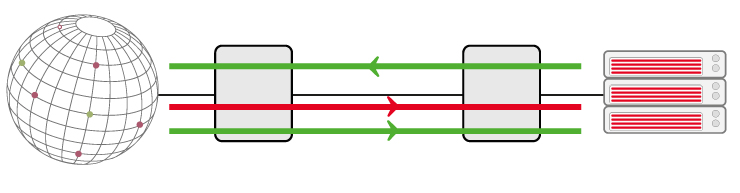
برای محافظت از سرورها و سرویس های شما در مقابل حملات، سرور مجازی فارسی یک سیستم مقابله برپایه تکنولوژی VAC ارائه می کند که شامل تکنیک های زیر است:
- Analyse: آنالیز تمامی بسته ها با سرعت بسیار بالا به صورت لحظه ای
- Vaccum: وکیوم کردن ترافیک ورودی سرور
- Mitigate: نمایش معضلات بسته های ارسالی از طرف آدرس های آی پی نامشروع
اهداف و انواع حملات DDoS
به طور کلی 3 راه اصلی برای از دسترس خارج کردن سایت، سرور و زیرساخت وجود دارد:
- پهنای باند: این نوع حملات برروی ظرفیت شبکه سرور تاثیرگذار هستند تا منابع مصرفی پهنای باند را اشغال نمایند و سرور را از دسترس خارج کنند.
- منابع: این نوع حملات منابع ماشین سیستم را به صورت کامل تخلیه می کنند تا سیستم قابلیت پاسخگویی به درخواست های ارسالی را نداشته باشد و عملا منابع آزادی بابت پاسخ نخواهد داشت.
- بهره برداری از مشکلات نرم افزاری: که به عنوان “exploit” شناخته می شود، این نوع حمله مشکل نرم افزاری خاص را مورد حمله قرار می دهد و سیستم را از دسترس خارج می کند و عملا سیستم کنترل خودش را از دست می دهد و توسط حمله کننده مورد کنترل قرار می گیرد.
| Name of attack | OSI level | Type of attack | Explanation of attack principle |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICMP Echo Request Flood | L3 | Resource | Also called Ping Flood, mass sending of packets implicating the response of the victim, which has the same content as the original packet. |
| IP Packet Fragment Attack | L3 | Resource | Sending of IP packets that voluntarily reference other packets that will never be sent, which saturates the victims memory. |
| SMURF | L3 | Bandwidth | ICMP broadcast attack usurping the source address to redirect multiple responses to the victim |
| IGMP Flood | L3 | Resource | Mass sending of IGMP packets (multi-cast management protocol) |
| Ping of Death | L3 | Exploit | Sending of ICMP packets which exploit an implementation bug in certain operating systems |
| TCP SYN Flood | L4 | Resource | Mass sending of TCP connections requests |
| TCP Spoofed SYN Flood | L4 | Resource | Mass sending of TCP connections requests to usurp the source address |
| TCP SYN ACK Reflection Flood | L4 | Bandwidth | Mass sending of TCP connections requests to a large number of machines, usurping the victim’s source address. The bandwidth of the victim will be saturated by the responses to these requests. |
| TCP ACK Flood | L4 | Resource | Mass sending of TCP segment delivery receipts |
| TCP Fragmented Attack | L4 | Resource | Sending of TCP segments that voluntarily reference other segments that will never be sent, which saturates the victim’s memory |
| UDP Flood | L4 | Bandwidth | Mass sending of UDP packets (not requiring a previously-established connection) |
| UDP Fragment Flood | L4 | Resource | Sending of UDP datagrams that voluntarily reference other datagrams that will never be sent, which saturates the victim’s memory |
| Distributed DNS Amplification Attack | L7 | Bandwidth | Mass sending of DNS requests usurping the source address of the victim, to a large number of legitimate servers. As the response is more voluminous than the question, an amplification of the attack follows |
| DNS Flood | L7 | Resource | Attack of a DNS server by mass sending of requests |
| HTTP(S) GET/POST Flood | L7 | Resource | Attack of a web server by mass sending of requests |
| DDoS DNS | L7 | Resource | Attack of a DNS server by mass sending of requests from a large set of machines which are under the attacker’s control |

![isometric-bg[1]](https://www.vpsfa.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/isometric-bg1.png)